
Cisco Vulnerability: A Potential Gateway for Hackers
A recently disclosed flaw in Cisco’s Integrated Management Controller (IMC) has raised concerns amongst businesses and individuals. Experts warn that this high-severity vulnerability could allow…
Affected Systems: Any system lacking in antivirus/malware protection.
Date Discovered: The ransomware has been developed and in use since July 2021. Microsoft posted the blog on 14th July 2022.
Details:
H0lyGh0st, a threat actor from North Korea, has been targeting small and medium businesses with a ransomware package of the same name. The group will use the ransomware to encrypt all files on a victim’s device and then send the victim proof of the stolen files using a .h0lyenc file. Notably, this threat actor will also threaten to publish the victim’s data online or send the data to the victim’s customers to coerce payment.
Microsoft has shared that some of the victims of these attacks include banks, schools, manufacturing organisations, and event planning companies. The attackers will ask victims to pay a ransom of anywhere between £2,300 to almost £10,000 in Bitcoin.
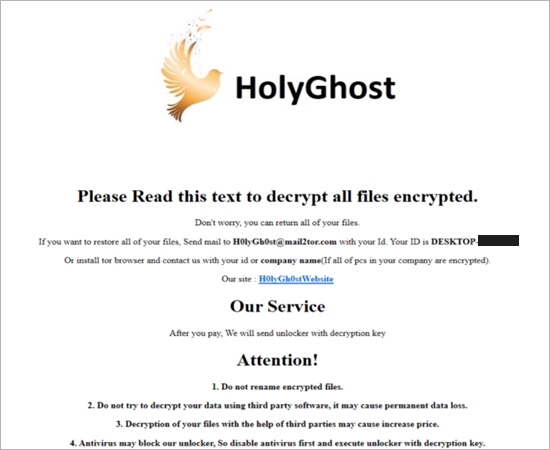
It should be noted that H0lyGh0st will often exploit vulnerabilities found on publicly available websites and systems to gain access to the victim’s network, taking copies of all files, after which the attackers execute the ransomware. However, Microsoft has not found any evidence of H0lyGh0st using zero-day exploits in their attacks, meaning attacks can be prevented by keeping operating systems and applications updated.
H0lyGh0st is known for developing several ransomware versions, the latest is able to connect to a network file share and create scheduled tasks to start the execution of the malicious code.
Preventions:
Microsoft directly notifies customers that have been targeted with this type of ransomware and will provide information to help secure their accounts. Additionally, it has been stated that the version of Microsoft Defender running on Windows 10 and 11 is able to detect and block all known versions of ransomware created by H0lyGh0st.
Microsoft encourages all organizations to proactively implement and frequently validate a data backup and restore plan as part of broader protection against ransomware and extortion threats.
Microsoft has published several indicators of compromise (IOCs) that have been seen in previous attacks. If possible, implementing systems that can detect such IOCs may prevent any attacks from happening, as well as showing any malicious past activity.
To prevent ransomware attacks SMEs should:
Read our Ransomware guide for more information on how to protect your organisation.
Related Links: